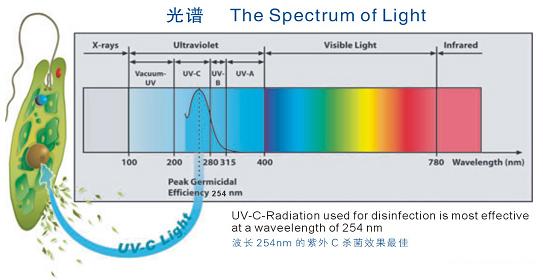
Light can be described as particles and waves, a phenomenon called wave particle duality. As particles, massless photons carry light energy (at the speed of light) throughout the universe. As a wave, energy radiates through the smooth oscillation of the electromagnetic field. Ultraviolet radiation is located in the short wavelength side of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 100nm to 400nm. The UV range is further subdivided into four categories: UV-A (315 nm to 400 nm), UV-B (280 nm to 315 nm), UV-C (200 nm to 280 nm) and vacuum UV (100 to 200 nm).
Vacuum ultraviolet wavelengths are so named because of their strong absorption, even through the air. Ultraviolet -A wavelengths, resulting in tanning, used for tanning salons (Nelson et al. 2016), are also commonly used to solidify anything from ink or paint adhesives and nail polish (Endruweit 2006). The energy carried by light is inversely proportional to its wavelength: therefore, the shorter the wavelength, the higher the energy. Therefore, the wavelength of UV-B radiation is shorter than that of UV-A, which has higher energy and higher cancer risk for human beings (NTP, 2016). Even the high-energy radiation in ultraviolet C band is most commonly used for disinfection. The sensitivity of most microorganisms to radiation is about 265nm, so the application of ultraviolet disinfection aims at the "bacteria" range around the peak.